Wastewater Treatment | Adhesive & Sealant manufacturers | Supex India
Industrial Adhesives Sealants used in wastewater treatment plants
An industry that consists of facilities and plants in large and small populated areas where wastewater treatment is needed.
- The wastewater treatment industry consists of plants whose goal is to provide waste water treatment services to the population. The average wastewater treatment plant employs 3-10 maintenance personnel responsible for the maintenance of pumps, containment areas, equipment and facilities associated with the treatment of wastewater.
- A water treatment plant size and planned capacity is determined by the population of the area in which it services. The quantity output is measured in gallons treated per day or per week. As the population of an area increases the larger a plant must be made or a new plant must be built.
- To make a current plant more reliable means that the life cycle of the plant can be extended and the mean average of water treated between breakdowns can increase.
Industry Statistics – Definition and Classification of Water Treatment Industry
- A plant that treats 20-35 million gallons per day ( a plant for a city of 40,000) will have 3-10 maintenance personnel and would be considered a medium size plant.
- A plant that treats 175 million gallons per day (a plant for a city of 1.5 million plus) can have 70-100 maintenance personnel, 10-30 electricians and up to 30 facilities and fleet maintenance personnel and would be considered a large plant.
A water treatment plant will employ approximately 10 maintenance personnel and or engineers/electricians to maintain and repair equipment.
Typical areas of concern in a water treatment plant involve the consideration of caustic materials, corrosion, mechanical abrasion and the containment of materials while in the treatment process.
Currently populations are growing faster and the demands on treatment plants are increasing. In response to this, new plants are being built and older plants are being retrofitted to increase their treatment capacity. The result is larger plants with more equipment and capacity
The most common maintenance functions are the repair and upkeep of pumps, concrete and transport systems on the facility (Conveyors, pipes, hoppers).
The industry has responded to this by looking for repair materials that will extend the life of their equipment and prevent common leaks, corrosion and loosening.
Wastewater treatment process
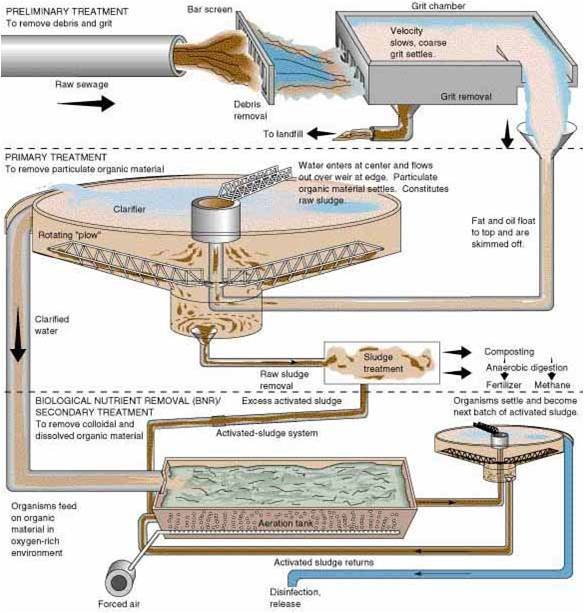
Description of Common Equipment in the sewage Treatment Industry
Conveyance System The Sewer Lines
This system consists of hundreds of miles of sewer pipe and drainage pipe that route the water from homes, businesses and streets to the wastewater treatment plant.
This entire system of pipes and man holes contains Supex applications
for Coating, corrosion prevention, Sealants and repair epoxies.
Pump Station
Gravity will carry the water from homes to the treatment plant. When slopes have to be overcome pumps in a pump station along the sewer lines boost the water and raise it over the slope.
The pumps at a pump station can range in size from a 2 inch discharge to an excess of 14 inches. These pumps are located in stations in areas where wastewater is collected and must be assisted via the pump in order to reach the treatment plant.
Bar Screen
 This piece of equipment consists of bars that screen out trash and large contaminants from the water as it enters the treatment plant. The screen at left has captured a tire and removed it from the water before it entered the plant.
This piece of equipment consists of bars that screen out trash and large contaminants from the water as it enters the treatment plant. The screen at left has captured a tire and removed it from the water before it entered the plant.
Grit Chamber
These concrete chambers slow down the flow of water after it has passed through the bar screen. Organic material stays in suspension as the mixer turns the water but sand, rock glass, metal and other grit will settle out. The remaining water moves through the treatment process.
slow down the flow of water after it has passed through the bar screen. Organic material stays in suspension as the mixer turns the water but sand, rock glass, metal and other grit will settle out. The remaining water moves through the treatment process.
Screw/Auger Press
An auger in a chamber will mechanically press water from debris and grit that has been filtered from water entering the treatment plant. 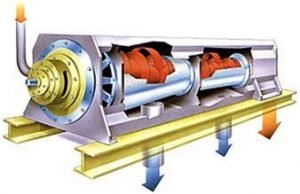
Separated solids are taken to a landfill (shown in red) and the water (shown in blue) continues through the treatment plant.
De-watering Centrifuge
 Sludge (water and solid waste) enter the centrifuge and like a large washing machine on spin cycle the material is flung at high velocities against the side of the drum. The separated water (in blue) continues through the plant and the “cake” (de-watered material shown in red) is mixed with compost and/or fertilizer.
Sludge (water and solid waste) enter the centrifuge and like a large washing machine on spin cycle the material is flung at high velocities against the side of the drum. The separated water (in blue) continues through the plant and the “cake” (de-watered material shown in red) is mixed with compost and/or fertilizer.
Clarifier
These cone shaped concrete chambers are common at all sized water treatment plants. 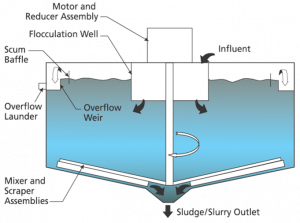
A scraper will remove the scum from the top of the water while
a urethane spatula will scrape
the heavier sludge from the bottom. The “cleaned” water moves up and to the outer
edges to continue through
the treatment plant.
Sludge Pumps
Each plant may contain up to
400 pumps of different sizes and configurations and for different purposes.
A sludge pump will pump water that is filled with solids (sludge) to the next step in the water treatment process.
Recurring maintenance issues
- Mechanical failures due to fastener & bearings loosening
- Corrosion of metal parts
- Erosin of pump casings
- Gasket failure
- replacement of worn out parts


Adhesives and sealants used
- Engineering adhesives : Threadlocker, threadsealants, bearing retainer, flange sealants
- Rebuild and repair metal epoxies: Steel putty, Titanium putty
- chemical resistant coatings
- Adhesive for general metal, plastic, rubber bonding
- anti seize chemicals
- maintenance sprays eg: rust loosener and lubricant
- silicone and PU sealants for sealing and bonding

