Construction Sealants at best price | Supex | India
Construction sealant definition & functions
Sealants are materials that prevent fluids and other substances from passing through surfaces and mechanical joints. Sealants also block air leakage, insects, dust, sound, and heat. There is a wide variety of sealants available in the market and their characteristics differ: they can be weak or strong, flexible or rigid, and temporary or permanent.
Sealants are typically used to close openings between surfaces, where other materials like concrete and mortar can’t be used. They serve three basic functions:
- Filling the gap between two or more components
- Providing a protective impermeable barrier, through which substances cannot pass
- Maintaining their sealing properties through their expected lifetime, under the service conditions and environments for which they are specified
To achieve these functions, it is necessary to match the most suitable sealant with the materials that will be joined.
Sealant Properties
When selecting a sealant, these are the most important properties to consider:
- Consistency: Sealants with high viscosity will not flow much from where they are applied, even on vertical joints. On the contrary, low viscosity sealants can even penetrate into a substrate, they are used in horizontal joints, and can be self-leveling.
- Hardness: This describes the ability of a sealant to resist deformation. Note that hardness is inversely proportional to flexibility, and as hardness increases the flexibility decreases.
- Weather Resistance: High performance sealants can withstand extreme temperature, sun and moisture, while remaining flexible and performing as expected.
- Durability: Sealants have an expected life cycle under ideal conditions. However, note that these conditions are not achieved in some applications, especially when sealants are misapplied or incompatible with the substrate.
- Movement: Movement tolerance is shown as a percentage of the joint width. This is determined by the ASTM C920 Standard Specification for Elastomeric Joint Sealants.

- Modulus of elasticity: Usually, low-modulus sealants have high movement capability and vice versa. Low-modulus sealants are used for delicate substrates, while high-modulus sealants are used in cases consisting of static or non-moving joints. There is a wide sealant variety in terms of modulus of elasticity, so applications may vary.
- Adhesion: The ASTM C794 Standard Test Method for Adhesion-in-Peel of Elastomeric Joint Sealants tests the adhesion of elastomeric sealants, which is a crucial factor when selecting them. Manufacturers provide adhesion data for sealants with various substrates.
- Staining: Sealant components may stain certain substrates, especially those that are porous, such as natural stone. Testing sealants before application is recommended, even when manufacturers claim their product is non-staining.
- VOC content: Volatile organic compounds are respiratory irritants that may be present in sealants. Manufacturers have developed sealants with low levels of VOC, but this does not apply for all sealants, and the best recommendation is always checking the VOC content.
- Cost: Sealant prices vary greatly, depending on their performance levels and applications. It is important to note that replacing failed sealants is usually more expensive than choosing the correct sealant from the beginning. Match sealants to the performance requirements to avoid future expenses.
Find out more about the construction sealants by signing up here.
Types of Construction Sealants
There are several types of construction sealants. They differ in cost and applications, based primarily on the performance properties mentioned above and the substrate properties.
| Sealant | Properties |
| Latex |
|
Acrylic sealant |
|
| Butyl sealant |
|
| Polysulfide sealant |
|
| Silicones |
|
Polyurethane sealant  |
|
MS polymer sealants |
|
Why choose MS polymer sealant instead of Polyurethane,PU sealant?
The outstanding performance of MS polymer adhesive is recognised by industry professionals around the world.
MS polymer demonstrates numerous benefits over other products commonly found on the market today. From stronger bond strength to excellent workability, here are the advantages to using MS polymer over Polyurethane sealant:
Benefits of MS polymer
- Excellent UV, water,chemical, environment resistance
- Stronger final bond strength
- Isocyanate & solvent free
- Permanently elastic, even at low temperatures
- Good workability
- No shrinkage of cured product over time
- More responsive to increased moisture in substrates
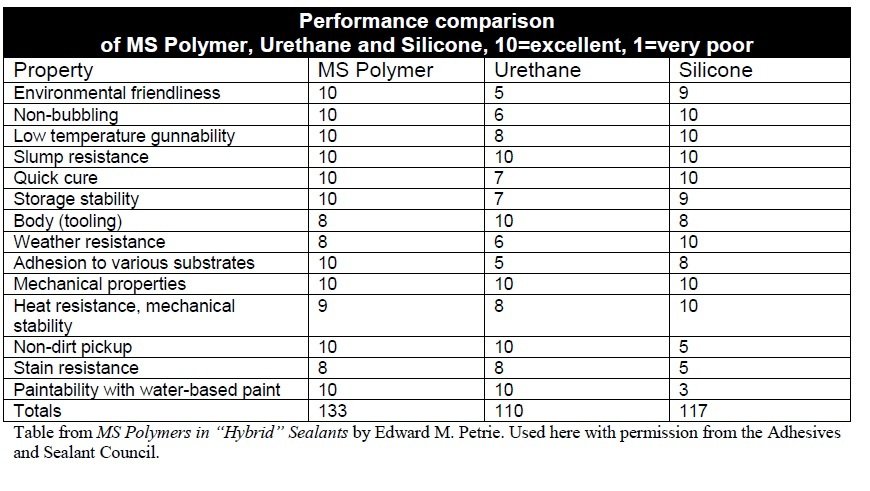
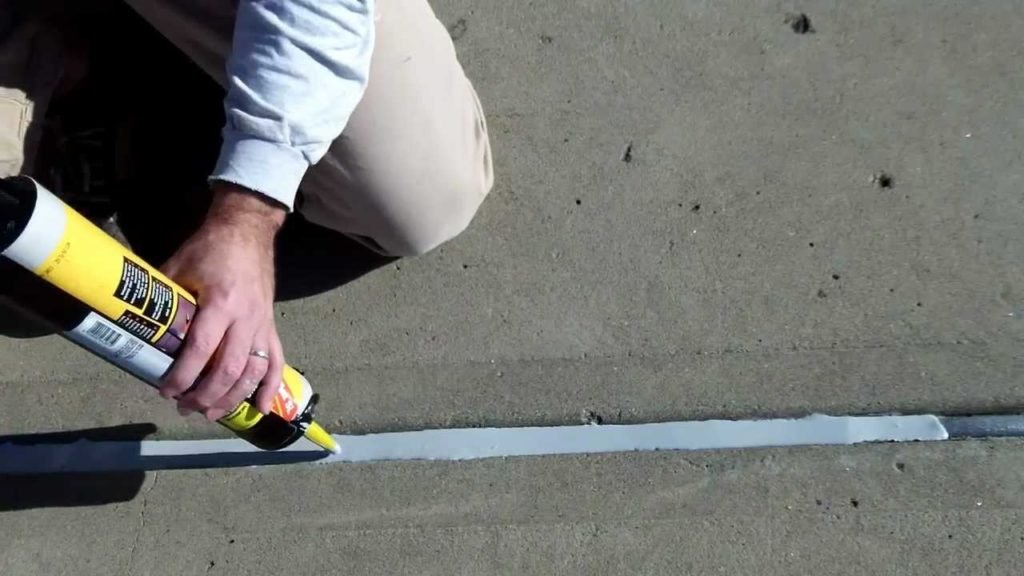
MS Polymer sealant and adhesive
1. LM MS sealant : An elstomeric hybrid sealant on advanced MS polymer technology. It is a Low modulus sealant with high movement capability and excellent weathering characteristics. Sealing concrete joints, precast wall panels, expansion joint, control joint, FRC board etc. Sealing anodized aluminium, masonry, porcelian, coatedmetal, finished wood, epoxy and polyester panels, upvc, polystyrene and stainless steel.
2. All in one MS sealant : Medium modulus elastomeric hybrid sealant based on advanced MS polymer technology. Suitable for high strength sealing & bonding in construction, automotive, marine, industrial applications. It works on various substrates like plastic, metal , rubber, natural material ( wood, leather etc)
3. Auto body seam sealant: A high performance elastomeric hybrid sealant based on advanced MS polymer technology. I t has fast drying speed, good UV & temperature resistance. Ideal for making permanent elastic seals of high bonding strength, expecially interior exterior auto bodyseams & joints.
A high performance elastomeric hybrid sealant based on advanced MS polymer technology. I t has fast drying speed, good UV & temperature resistance. Ideal for making permanent elastic seals of high bonding strength, expecially interior exterior auto bodyseams & joints.
4.  All clear MS adhesive: a clear colour MS polymer sealant formulated for bonding & sealing applications for long term reliability. It will bond to form a durable, flexible, waterproof seal. Ideal for bonding plastics, metal, rubber, wood , leather,paperboard, concrete etc.
All clear MS adhesive: a clear colour MS polymer sealant formulated for bonding & sealing applications for long term reliability. It will bond to form a durable, flexible, waterproof seal. Ideal for bonding plastics, metal, rubber, wood , leather,paperboard, concrete etc.
5. High perfomance MS sealant: is a Hybrid Silyl Modified Polyether technology based high grip one component strong adhesive. It is suitable for direct bonding on a wide range of heavy construction materials without support and able to hold up to 13 kg weight. That is why support of the adhesive assembly is not necessary in general. It has high performance mechanical properties and combines high stiffness with very high bond strength. It is recommended for usage in sealing and bonding in building and construction industry.
6. Primerless auto glass sealant: mositure cured high modulus MS polymer sealant formulated for windscfreen bonding applications. It has high green strength & excellent resistance against weathering & temperature extremes. It is solvent free and not shrink after curing.
7. MS flooring adhesive: is based upon Hybrid Silyl Modified Polyether Technology. it is an odourless, one part flooring adhesive suitable to bond many types of parquet flooring to almost any sub-floor. it has a high bond strength between the wooden floor and the sub-floor but remains permanently flexible. it is an ideal product for indoor and outdoor bonding and sealing purposes.
For knowing more about MS polymer technology you can sign up here.
Kindly post your questions/ queries in the comment section or contact me at:
Bibhas Agarwal
anaghaengineers.in@gmail.com
Whatsapp: 91 9833892782
Call : 91 9699892782
www.anaghaengineers.in
Metal bonding adhesive in India
Why metal bonding?
No matter what you design, from computers to cars, assembly is always a challenge. What is the lowest cost, highest performance technique for joining parts and subassemblies? When it comes to metal-to-metal bonding, options include thermal joining techniques such as welding, brazing or soldering; mechanical fastening with hardware; and bonding using a liquid adhesive or tape.
Each method comes with its own advantages and disadvantages, though they share many of the same applications. For example, when mounting metal panels to the metal frame of a machine housing, solutions include metal-bonding adhesive tapes, liquid adhesive, welding, or mechanical fasteners, such as rivets.
So, how do you decide which method to use for metal assemblies?
Metal-Bonding Adhesives vs Welding
Welding is a very common technique for metal-to-metal assembly operations, and in some ways using adhesive for metal is very similar. For example, the lack of protruding fastener heads gives both welded parts and glued metal parts a more streamlined appearance.
However, welding also has a number of disadvantages that would not apply to a metal-to-metal adhesive bonds.
Welding introduces many complications and problems which often aren’t immediately visible.
- Thermal distortion – Every weld pulls and distorts the final product and can cause cracking.
- Welder skill – Anybody can bolt two pieces of metal together but even the simplest welding requires skilled labour or automation
- Variables which change with material and joint type – Welding mild steel is fairly straightforward but if you are welding a high alloy steel or, other metals you will need someone who knows what they are doing. These variables include:
- Voltage, current, wire feed speed, travel speed
- Heat input
- Filler metal
- Preheat, postheat, inter-pass temperature
- Process
- Shielding gas, flux
- Hydrogen control
- Mechanical weld adjustments – Grinding, peening
- Ability to join dissimilar metals is limited at best
- Many problems are not visible – Testing methods are used to find these discontinuities. The main four are liquid penetrant and magnetic particle for finding surface or near surface problems and ultrasound and radiography to find subsurface problems. All these methods require skilled labour.
In contrast, most adhesive products can be correctly applied with minimal training. This translates to more consistent quality and lower overall production cost.
Find out more about the adhesive products that can replace costly welding by signing up here.
Metal-Bonding Adhesives vs Fasteners
Fasteners such as bolts and screws are very common methods of bonding for temporary joints. Fasteners are also suitable for semi temporary joints such as those in automotive assemblies. Nevertheless, problems may occur as fasteners require carefully placed holes, are prone to corrosion and may loosen over time.
This is where metal adhesives come into picture: removable adhesives and tapes are suitable for temporary bonding, and they do not leave traces behind after removal. Adhesives are also suitable for semi temporary joints as they seal from corrosion, are generally lighter and cheaper than mechanical fasteners, and distribute the stress throughout the bond making the assembly stronger. Some metal bonding adhesives come with special properties such as chemical resistance and heat resistance. Heat resistant glue for metal is common in public transport vehicles, automotive industry and general industrial applications. Metal glue can also be used for supporting fasteners: threadlocking and thread sealing are common applications where a metal glue makes sure the fastener does not loosen over time.
If your design uses fasteners, click here to receive more information about other adhesive options.
Types of metal bonding adhesives
- Epoxy adhesive is one of the strongest adhesives for metal. It exists in different types which have unique properties such as chemical resistance and heat resistance. Epoxies come as one or two component systems. Single component epoxy glue for metal cures as a result of additional heat. A 2K system is a mixture of two parts with react with each other starting the curing process. When looking for the strongest glue for metal, a 2K epoxy for metal should be considered.
Limitations:
- 2 part mixing is messy, time-consuming, not suitable for continuous production.
- Epoxy is brittle by nature, cant take vibrations or flexing
- labour intensive, application cannot be automated
- 2 part cartridge requires special gun applicator and still not user friendly.
- it has a typical smell
2. Acrylic adhesive metal glue exists as two types: surface activated and and bead on bead acrylics. The latter refers to applying a bead of adhesive on both substrates before connecting them. The bonding starts when the parts come in contact with each other and become subject to pressure. Surface activated acrylics, in turn, require a water thin initiator applied to one substrate and the resin to the other.
Limitations:
- 2part system- time consuming, not friendly for high speed production lines.
- limited flexibility, joints cannot be subjected to flexing
- adhesive cost is high
3. Cyanoacrylate, also known as instant adhesive, is the super glue for metal to metal bonding. Cyanoacrylate adhesives is suitable for most metals as long as they are reactive. Therefore, the super glue for metal works better on brass and copper than on steel. Due to the excellent performance as metal glue, commercial cyanoacrylate adhesives are very popular among miniature and modeling hobbyists.
Limitations:
- brittle bondline after curing, cannot be subjected to joint movement and flexing
- debonds or bond fails if in contact with water continuously
- health hazard- bonds to skin instantly, while curing it emits vapours with a strong smell, eye irritant
- not suitable for large bonding areas, cannot fill high gaps ( > 1 mm)
4. Anaerobic metal adhesives are only used for glueing metal to metal as they require the presence of metal and absence of oxygen to be able to cure. Anaerobic adhesives are ideal for securing fasteners in terms of thread-locking and thread sealing as well as gasketing and retaining.
Limitations:
- cannot be used for high gap fill applications eg: sheet metal bonding
- cured adhesive is not flexible so cannot withstand flexing and joint movement.
- Suitable only for specific engineering application only. Not suitable for typical large surface area bonding
- Doesn’t work with non-metal substrates
5. Polyurethane sealant and adhesive : PU sealants are excellent for bonding / sealing metal to metal joints. In fact, in India, it is a popular adhesive used as a bodysealant for busbody manufacturing. It has high elongation, flexibility, bonds well on metals, paintable and at affordable cost too.
Limitations:
- Generally not UV resistant
- Degrade over time, typical life is 5 years and needs replacement.
- Bond strength not the best. It is primarily a sealant that bonds too.
- Not good environment or weather resistance.
- contains solvents, not VOC free.
6. MS polymer adhesive : This chemistry was developed to combine the weathering/ environment resistance of Silicones and high gap fill, flexibility, paintability of Polyurethanes. Also it is solvent and Isocyanate free, high strength with high elongation, paintable, UV resistant. It is a verstile bonder and bonds to most building material and engineering substrates except telfon, PP, HDPE, LDPE. This technology is already a dominant player in Japan, gathering pace in USA, Europe. It is widely used for automotive, Industrial and construction applications.
Limitations:
- Product cost is higher than Silicone or polyurethane sealants.
- Temperature resistance, works upto 100 C. is lower than RTV Silicones.
Bonding Metal to Metal
Structural adhesives can also be applied quickly and easily, such as with a dispensing gun, though they require curing time before the bond reaches full strength. Using faster, simpler assembly techniques can reduce labor and training costs, consequently reducing physical demands on human workers.
Another advantage of using adhesives in metal-to-metal applications is that they seal, potentially eliminating unnecessary steps in the assembly process. This seal can even be flexible, allowing for relative movement of parts without weakening the bonds. This makes adhesives suitable for applications involving temperature changes, weather and vibration, such as with many automotive and consumer goods.
The number of instances where adhesively bonding metal to metal is the most cost-effective solution may surprise you.
Surface Preparation for Metal Adhesive Bonding process
Selecting the best adhesive for your metal-to-metal application can be difficult. Different metals subjected to different environmental conditions will consequently behave very differently. As a result, there is no such thing as the strongest adhesive for bonding metal. That’s why it’s important to choose the right adhesive based on a number of design considerations.
Most metals have relatively high surface energy, allowing adhesives to wet the surface and thereby improving bond strength. However, painted and powder-coated metals present a different surface.
On a painted surface, the adhesive is not bonding to the metal but instead to the paint coating. Nevertheless, it’s possible to achieve a successful bond to the metal or its surface coating, depending on the bond strength you need. One option is to mask the mating surfaces before coating, preserving the metal surface. Another is to choose an adhesive solution appropriate for bonding directly to the painted metal.
A “powder coat” is an electrostatically applied resin to a metal surface, heat-cured to form a solid layer. Powder coats are significantly more difficult to bond than paint because they often present a lower-surface-energy substrate. This will affect the adhesive you choose.
Adhesives form the best bond to clean, dry, oil-free surfaces, including oils from workers’ hands touching the surface.
It’s also important to consider the surface condition of your substrates. Rough surfaces can make for stronger mechanical bonds by increasing the surface area of the joint or removing residual contaminants much better than cleaning alone.
However, this benefit is only realized if the adhesive can penetrate the small cracks and fissures and wet the entire surface. A bonding tape, for example, is not able to wet deep inside cracks or around raised scratches of aggressively abraded surfaces. Therefore, a liquid adhesive is best for highly abraded surfaces. Metal Bonding – Which Process?
When selecting a method for metal-to-metal bonding, the most important thing to keep in mind is how your chosen method will fit into your assembly process.
Are you looking for a solution that will fit into your current workflow, or can the workflow change to accommodate the new solution?
In addition to assembly considerations, you should also think about how the final product will be used.
All of these considerations—the assembly process, end use and overall cost—need to be taken into account when selecting an adhesive for metal bonding.
Want more helpful content like this from Anagha Engineers? Sign up to stay in touch!
Kindly post your questions/ queries in the comment section or contact me at:
Bibhas Agarwal
anaghaengineers.in@gmail.com
Whatsapp: 91 9833892782
Call : 91 9699892782
www.anaghaengineers.in
Foam Spray Sealant | Uses, types, advantages of PUF | Supex India
Type of Foam Spray Sealant
PU Insulating Foam Sealant is generally made available in two forms –
- Spray Can – Dipensed using an adopter or straw or Pipe : one straw is preattached to the can .
- Gun grade – Dispensed using a Hand held PU Gun
Using Spray Can- Foam spray sealant

- Clean the application area with water spray.
- Moisten the area with Water spray. PU foam adheres to almost all surfaces that are strong, clean and free of dust and grease. Only silicon, oils, greases, polyethylene, teflon or similar surfaces are not suitable to be applied on.
- Surface must be dampened enough to ensure that the foam sealant finds adequate moisture for its hardening process. Otherwise, it could impair the adhesion and edge adhesion.
- Attach the Straw on the can.
- Shake the can vigorously for 20 to 25 times.
- Hold the can upside down such that the valve faces downwards. This is the only way to completely empty the can.
- Press the trigger, foam will rush out of the can under pressure.
- Keep shaking the can.
- Plan the work such that entire can material is consumed in one go, i.e., after opening the can, it should be completely consumed. This is recommended because whatever is left will get cured inside the can and thus go to waste.
- The foam cures in 30 – 40 minutes depending upon weather conditions.
- After curing , extra foam can be cut with a sharp knife.
- Foam sealant is paintable. It is not UV resistant – should not be exposed to direct sunlight. If unavoidable – paint the foam to protect from sunlight.
Using Gun Grade foam spray sealant
 Clean the application area with water spray.
Clean the application area with water spray.- Moisten the area using the same water spray. Foam sealant adheres to substrates that are clean and free of dust and grease.
3. Surface must be dampened enough to ensure that the  Foam sealant finds adequate moisture for its hardening process.
Foam sealant finds adequate moisture for its hardening process.
4. Attach the gun on the spray can, hold the gun such that the can is upside down .
5. Adjust the knob at the end of gun to control dispensing speed/ quantity. Press gun trigger for application.
6. Keep shaking the can.
7. Gun mounted can be used and stored for a day or two , provided the tip of gun is sealed from moisture – using grease etc.
8. The foam cures in 30- 40 minutes depending upon weather conditions.
9. After curing, extra foam can be cut with a sharp knife.
10. PU foam sealant is paintable. However, it is not UV resistant – should not be exposed to direct sunlight. If unavoidable – paint the foam to protect from sunlight.
11. After emptying the can , mount the PU cleaner – press till entire foam is extruded from the gun and the gun is free from foam .
12. Gun and cleaner can be removed and stored till next usage.
Applications of Foam Spray Sealant
- Filling of joints, seams and cracks in partition walls with ceilings.
- Structural space between window and door frames and walls.
- Structural and fitting space between prefabricated construction elements
- Around cables and pipes, penetrations through walls and ceilings.
- Gluing panels/ insulating sheets.
Which Industries Require This Product?
- Construction: Fitting Door frames, window frame gaps, sealing tie rod holes/joints, gap between bricks and beam, bonding AAC blocks.
- Power plants: Sealing gap between cable and wires, gap between electric panel outlet.
- Solar Plants: Sealing gaps between cable and wire.
- Interiors: Gap filling.
- Terrace: heat insulation.\
- Cold Storage/ Wooden houses: Gap filling purposes.
Kindly post your questions/ queries in the comment section or contact me at:
Bibhas Agarwal
anaghaengineers.in@gmail.com
Whatsapp: 91 9833892782
Call : 91 9699892782
www.anaghaengineers.in
Door Frame fixing with Gap Filling PU Foam Spray.
Need for gap filling PU foam spray?
Window and doorframes are made of materials such as wood, aluminum, steel and UPVC. Traditional window and doorframes are installed by using frame anchors and gaps filled with white cement/ putty. This method
- Is time consuming and requires craftsmanship.
- Cement/ Putty tend to crack over time due expansion/ contraction cycle of construction joints
- poor aesthetics
- Entire load is shared by the anchor fasteners, due to excessive stress at few points stress failure may lead to door frame failure.
- Installation is unrelaible and cost is also high.
Using polyurethane foam sealant can significantly reduce labour costs and improve strength of door frame.
Advantages of PU foam spray vs traditional methods

- provides increased structural strength to the door frame due to high bonding strength. You can reduce the number of anchor fasteners used for fixing the door frame.
- PUF is not rigid like white cement or putty, hence the joint doesnt crack with time due to expansion & contraction.
- Lower labour cost due to fast process.
- Higher productivity
- additionally provides sound and thermal insulation.
- can be cut with a knife, sanded, painted like normal gap filling putties. Finish or aesthetics is much better than other regular methods.
- Overall lower cost
Gap filling PU foam for Door / window frame installation
What is a good quality PUF Sealant
- Density of cured PU foam, high density pushes the door frame while low density puf shrinks due to load. Ideal: 25- 30 Kg/m3
- Output of foam generated per 750 ml can, joint yield. Length of joint covered with 750 ml can is approximately 30 meters. It may vary depending on the gap width & depth between door frame and wall.
- Cellular structure – 70% closed cells
- Weight of 750 ml can: 850 gms, sometimes cheap products avaialble fill lesser PUF in the can to reduce price.
- Skin formation : 8-10 minutes
- Cutting time: 25- 35 minutes, affects productivity.
- Fire rating: B1 or B3 , B1 grade is at least twice expensive than B3 grade since B1 is FR PUF- it retards fire upto 120 minutes and it duly approved after testing conducted by a reputed institite. Product data sheets can mention FR data however 3rd party test report for B1 grade is essential.
Is Gun grade PUF sealant better than straw grade pu foam can for door frame applications ?
Ideally, Gun grade is the better option than adopter/straw grade PU foam spray cans.
Why.
1. Gun type PU foam sealant is designed for lower expansion and high bond strength – this is essential for door frame fitment. Lower expansion ratio ensures that puf doesnt exert pressure on door frame, high bond strength improves structural strength of door frame.
2. Gun helps in controlling the quantity of Puf used so the wastage is lesser.
Charactersitics of PUF sealant
- Single component product, doesn’t require mixing etc
- mildly flexible, can withstand vibrations, building movements
- Bonds all building material, high bond strength
- high gap filling ability upto 50 mm or more – no sealant has this ability
- Excellent stability ,doesn’t shrink, doesn’t sag on vertical surface
- covers large area due to high expansion ratio
- Excellent Thermal, electric, sound insulation
Door frame installation process
A. Material Required
- Water spray can
- Supex Masking tapes
- Brush
- Cutter
- Spacers (optional)
- Supex 100 PU foam sealant
- PU Foam Gun Applicator and Cleaner (if you are using the Gun Grade version)
B. Applying Gap filling PU foam for door frame fixing
STEP 1: Preparation:
- Keep a gap of minimum 10mm and maximum 20mm between and door frame.
- Substrates should be clean and free of dust and grease but can be moist.

- Loose parts must be removed and if necessary primer must be used (e.g. old plaster)
- Slightly humidify the surface & door frame before applying the foam

- Use protective gloves
- Shake can thoroughly for 30 seconds
STEP 2: Applying of PU foam spray sealant:
- Hold the can upside down and extrude the PU foam by pressing the bar

- Spray some extra water if you are filling a gap with some depth or if you are applying the foam in different layer.
- PU foam sealant is a moisture curing product, it will cure by absorbing moisture from the air. Spraying some water on the wall and frame will fasten-up the curing process and will give a better cell structure (acoustic & thermal properties)
STEP 3: After applying PU Foam sealant
- Spray some additional water on the applied PU foam on both sides of the frame
- After use, clean the valve and tube immediately with Gun & Foam Cleaner
- Cut the spoiled foam away after curing of PU foam (24 hours)
- Let the foam cure for minimum 24 hours before putting the door in the frame
Important facts about Gap Filling PU foam spray:
- Always store cans upright.
- Store in a cool and dry place at temperatures between +5°C and 35°C
- Never put a PU foam spray can in direct sunlight
- PU foam spray sealant is not UV resistant so it always needs to be covered with a sealant, paint or plaster.
- Strong bonding characteristics
- Excellent adhesion on most common materials and between different materials
- Effective thermal and acoustic insulation
- Wonderful filling capacities, expands to 40 times its original volume
- Electric insulator
- Environmentally friendly (CFC-free) propellant gas
FAQ’s on Door frame installation with gap filling PU foam spray
Is it necessary to moisten the surface before using expanding foam sealant ?
We recommend moistening because the system needs water to cure. Other benefits one will get: i. Better cell structure ii. Better adhesion iii. Faster curing iv. Better foam quality
Is there a negative effect on insulation spray foam sealant if the can is not shaken thoroughly prior to use?
Polyurethane spray foam consists of a prepolymer and a propellant gas, which form two layers during storage. The can must be shaken vigorously before use to create a homogeneous mixture. Insufficient shaking will result in poor foam properties such as a coarse cell structure and reduced foam volumes.
Does the Polurethane foam can need to be shaken again during use?
It is recommended to shake the PU spray can occasionally during use, and especially after interruptions, to avoid re-separation of the propellant & prepolymer.
Is it OK to leave half-empty canisters attached to applicator guns?
Yes; in fact we recommend leaving a partially-full container attached to the gun. To store the gun and pu spray can safely, the security screw should be tightened to secure the trigger.
What is the purpose of Remover? Can any other material be used?
Remover is used to clean the dispenser gun and the needles. The Remover can be mounted on the dispenser gun, thus cleaning the dispenser PUF gun more effectively. By using any other material the chances of damaging the pu spray gun increase.
How easily can a window mounted with PU Foam sealant be removed?
Window mounted with PU Foam sealant can be removed easily by slicing through the foam, but removal of the window by force is near to impossible.
Does the polyurethane foam spray sealant develop and exert pressure during expansion and curing?
Yes, the PU foam exerts a pressure during expansion and through hardening. It is therefore advisable to fill gaps and cavities by no more than one third.
What should I do with excess pu foam sealant such as that round doors and windows?
Cured excess polyurethane foam can be cut away with a knife, saw or any similar implement.
From where do I buy Pu foam spray in Mumbai / India
Anagha Engineers products are available in Mumbai and across India. Just call +919833892782 for best price, training and swift technical support.
Which is the best PU foam sealant for door frame fixing available in India?
Supex 100 PU foam – gun grade or straw grade is a high yeild, versatile product manufactured with German technology. Anagha Engineers has various PU foam sprays used for general industry, Solar, construction segments.
When NOT to Use Spray Foam Insulation
- For areas that are too close to electrical boxes:
- For areas too close to ceiling light boxes: You should not use spray foam to insulate areas around recessed ceiling canister lights. …
- Open-cell spray foam on your roof: …
- For closed-cavity spaces: …
- If you have a history of skin, respiratory, or asthma problems:
How to contact Anagha Engineers application experts?
Call 9833892782 for:
- Site demo
- free samples
- technical discussions
- price
- order
Adhesives Technology | Types, Uses, Advantages | Supex India
Why adhesives- Advantages of adhesive technology over traditional methods
Adhesives bond dissimilar and hard to bond materials
Adhesives can bond hard to bond materials such as low surface energy plastics, oily metal and silicone rubber. Without adhesives, it would be difficult to imagine how to assemble two dis-similar material like plastic to rubber, metal to wood, plastic to metal etc
Adhesives bond and seal simultaneously
Using adhesives to bond two surfaces helps seal out water, moisture, dirt and other environmental contaminants. Because the seal has adhesive properties, there is no need for a separate mechanical fastener.
Adhesives reduce stress concentration at screw and rivet points
Mechanical fastening requires drilling holes, and attachment at each hole concentrates stress at that point. Because adhesives and tapes bond over an area rather than points, they disperse the load over the entire bond area. Eg: entire bus body is made from adhesive and sealants- sheet metal bonding instead of fastening or welding.
Adhesives improves production efficiency
Incorporating adhesives into the manufacturing process can improve efficiency by eliminating process steps, failure rates, and time of assembly. Adhesives can increase speed, reduce cost, reduce labor hours and streamline operations.
Adhesives improves aesthetics
Adhesives provide virtually invisible fastening to keep surfaces smooth and clean with no visible screws, rivet heads or protruding nuts and bolts. Adhesives also save the time and cost of refinishing welding burn marks. Eg: bonding glass to glass with optically clear adhesive.
heads or protruding nuts and bolts. Adhesives also save the time and cost of refinishing welding burn marks. Eg: bonding glass to glass with optically clear adhesive.
Adhesives reduce vibration, fatigue and noise
Because adhesives are viscoelastic, they are energy absorptive and improve the impact, vibration and fatigue performance of your design.
Types of adhesives
Adhesives are primarily classified based on their curing mechanisms and chemistry.
Based on curing mechanism
Water based adhesives– cure ( dry ) when water evaporates from the adhesive. Eg: Fevicol white glue used for plywood bonding in interior furnitures
Solvent based adhesives – cure ( dry ) when solvent evaporates from the adhesive. Eg-rubber adhesive used for type puncture repair, shoe repair.
Non curing adhesives : Eg: butyl sealant for bonding car door fabric to metal body.
Reactive adhesive– cures when it reacts due to some external factor( eg- UV curing glue) and chnages phase from liquid to solid. Eg: 2 part araldite cures after expocy and hardener are mixed together.
Based on chemistry
Acrylic adhesive – Generally 2 part adhesive system for structural bonding.
Anaerobic adhesive – one part adhesive used for threadlocking, threadsealing, flange sealing, bonding cylindrical assemblies. Used extensively in manufacturing and maintenance work. It is also called Engineering adhesive.
Cyanoacrylate adhesive  – popularly called instant adhesive or super glue. It bonds instantly. It can bond alomost all material except telfon. It is not flexible after curing and generally used for bonding small parts.
– popularly called instant adhesive or super glue. It bonds instantly. It can bond alomost all material except telfon. It is not flexible after curing and generally used for bonding small parts.
Epoxy adhesive –  Araldite is a polular household name in India. It is used for bonding any material together. Generally 2 part system which either is mixed manually or used with a special 2 part dispenser.
Araldite is a polular household name in India. It is used for bonding any material together. Generally 2 part system which either is mixed manually or used with a special 2 part dispenser.
Methyl methacrylate adhesive – 2 part adhesive system used for structural bonding.
Silicones– Silicone adhesive and sealant is popularly used for glazing applications. Some viscous silicone sealants are used for other bonding purpose also.
Polyurethane adhesive – It is a single component adhesive used for wood working applications, honeycomb bonding and other furniture manufacturing applications.
PVA ( Poly vinyl acetate) – Typical white glue used by students for project work like paper pasting, carboard pasting and sundry home use.
Synthetic rubber adhesive – Dendrite is a poplular SR adhesive used in India. It can bond most substrates. It is also used for bonding solid gasket on the flange.
Hot melt adhesive – There are various types of hot melt adhesives used for book binding, wood working, packaging, automotive interior assembly, diaper and sanitary pad production etc.
MS polymer adhesive
 MS polymers is the latest generation adhesive and sealant which combines advantages of silicones and polyurethanes. It can be used for bonding almost all materials except pp,teflon,hdpe, ldpe.
MS polymers is the latest generation adhesive and sealant which combines advantages of silicones and polyurethanes. It can be used for bonding almost all materials except pp,teflon,hdpe, ldpe.
Advantages of MS Polymer adhesive
- High initial tack properties reduce the need for initial support.
- Fast curing, a quick build-up of end strength alongwith high sheer strength after full cure (no primer).
- Easy to apply and easy to tool and finish
- Remains elastic after curing.
- No odor.
- Does not contain neither isocyanates, silicones nor solvents.
- Paintable with all water-based paints.
- Excellent color stability. Likewise, weather and UV resistance.
- Good adhesion on wet substrates, bonds underwater.
Adhesive selection parameters
MSECP
M- Machine – How are you applying the adhesive? How Fast? What type of equipment are you using?
S- Substrates – What are you adhering together? E – Environment– What will the bond / finished product be subjected to? (Hot Fill, Cold, Wet, Freezer, Blast Freezer) C- Cost and volume – Ballpark of where you would like this product to fall in your COM. How much & how often do you order?
P- Plant conditions– What are the conditions in your plant? (Temp Controlled, Dusty, Wet, ETC.)
Summary of questions to be answered for adhesive selection.
- Details of the substrates to be bonded- low energy substrates like telfon, HDPE, LDPE, PP is diffcult to bond and requires special surface prepration before bonding.
- Gap between the surfaces- for higher gaps than 0.5 mm we need higher viscosity adhesive, else regular CA( cyanoacrylate, instant glue) will work.
- Max Temperature to be sustained by the assembly – If more than 100 Celsius: silicone adhesives are the best else you have to select special high temperature grade from other chemistries.
- Type of loading, stresses on the adhesive joint – instant glue is not good in cleavage, peel or shear strength.
- Production speed: How many assemblies per hour to determine how to dispense the glue.
- Environment: Will the adheive bondline come into contact with water, fuel, gas, harsh chemicals etc. knowing this we need to choose adhesive chemistry that can sustain that environment.
Kindly post your questions/ queries in the comment section or contact me at:
Bibhas Agarwal
anaghaengineers.in@gmail.com
Whatsapp: 91 9833892782
Call : 91 9699892782
www.anaghaengineers.in
How to select right Sealant at best Price | Supex India
How to select right Sealant at best Price | Supex India
- engineers
- September 12, 2019
Table of Contents
Sealant Terminology
ASTM C 920 is the standard specification followed across the world for elastomeric joint sealants. Put together by American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM); it is made up of several ASTM test methods including:
- Movement capability (ASTM C 719)
- Sealant hardness (ASTM C 661)
- Tack free time (ASTM C 679)
- Adhesion in Peel (ASTM C 794)
Movement Capability – ASTM C 719
It is a standard designed test to measure the degree of cyclic movement (extension [+] and compression [-]) that a sealant can undergo in stimulated weathering conditions. Depending on the test results, sealants get further classified into the following movement classes
- +/-12.5% – write what class of sealants come in this range.
- +/- 25%
- +/- 35%
- +/- 50%
- +/-100/50%
Sealant Hardness – ASTM C 661
It is the standardized test to measure a sealant’s ability to resist the penetration by a Durometer probe. The rating scale for the test ranges from 0 to 100, with the lower rating meaning that the material is more softer. The less hard the sealant, the more movement it can accommodate. n
In the same fashion, the higher the number, the harder the sealant is, and the less movement it can take.
Stress Relaxation
It is the standardized test to check if the sealant can absorb extension without sustaining additional stress on the substrate’s bond line. Sealants which are can recover quickly and entirely from deformation report lesser stress relaxation numbers than those that recover slowly.
Modulus
Sealants with low modulus index indicate that they create low stress at the sealant bond line. It is usually associated with a higher movement capability.
Medium Modulus sealants are typically used for general purposes and are applicable for the majority of elastomeric sealant applications. High Modulus sealants generally are not used for moving joints. Preferably, they can be in glazing applications.

- Gap between the joints in mm
- Flexibility of the joint depending upon if it is subjected to expansion/ contraction
- Exposure to external environment . Viz :
Sunlight – is it UV resistant - Chemical resistance : exposure to corrosive chemicals, acids, fuels etc
- Temperature to be sustained by the assembly
- Expected life of the joint : sometimes sealants are used temporarily to hold parts together
- Paintability – can it painted over
- Cost/ Price of the product and application
- Ease of application
Types Of Sealants

Silicone sealant
It is the most popular type of sealant used. The silicone variant checks all the boxes for the factors required when it comes to choosing a sealant. It is seen to be extensively used in manufacturing, maintenance, construction, interiors and in any sealing application.
Advantages of Silicone RTV sealant
- UV stability.
- Color stability.
- Adhesion to variety of construction surfaces.
- Exceptional high movement accommodation.
- Extreme temperature resistance.
- High workability.
Silicone sealants are further classified based on their curing systems
![]()
Acetoxy Silicone sealants
- Acetoxy Silicone sealants-Most popular & used extensively due to lower price.
- Disadvantages: not sensor safe, corrosive due to acetic acid vapours released during curing, cannot be painted over, strong smell.
- Uses of acetoxy silicone sealants: Gap-filling, high temperature (300°C) sealing, any general-purpose sealing/bonding application.
Range of Acetoxy silicone sealants from Anagha Engineers
- Supex 200GP – 260 ml
- Boss Flexsil GP- 260 ml
- Boss 122 GP- 260 & 280 ml
- Mccoy Soudal GP – 260 & 280 ml
Colours avaialble: Clear, White and black
Neutral cure silicone sealants
Neutral silicone sealants are higher grade Silicone sealants used for technical and critical applications.
- Applications: Flange sealing in Automobiles, manufacturing, Plant maintenance, Food and Pharma plants for general bonding/sealing, External window gap sealing, Glass Bonding, glazing , weather sealing.
Neutral plus silicone sealant from Anagha Engineers:
- Supex Neutral plus, 260 ml
- Boss 396, 270 ml – similar to Dowsil Neutral plus
- Boss 395, 280/ 300 ml. Industrial grade, flange sealing, high temperature RTV
- Mccoy Soudal Neutral + , 270 ml
- Silirub PS, 280 ml
- Silirub B&K – Bahroom & kitchen sealant
- Silirub WSL+, weather silicone
- Boss 388- weather sealant, high bonding strength
- Boss 389- weather silicone
Polyurethane Sealants/ PU Sealants
Characteristics of PU sealants
High gap filling, high bonding strength, flexibility , chemical resistance, weatherability, can be painted over.
Uses/ applications of PU sealants:
- Construction: Expansion Joint sealing, internal joint sealing ( Eg: isolation joints)
- Windscreen Bonding: most popular application for PU sealants used in Automobiles, Railways. Glass to metal bonding.
- Automotive industry: for Bonding Panels in Bus body building, high vibration resistance ( sound deadening sealant), high bonding strength, flexible bonding,
- General Manufacturing: HAVC, Elevators, escalators – sheet metal bonding, panel bonding, general high strength flexible bonding
Acrylic Sealants
What is an acrylic sealant?

Paintable acrylic sealant is a multipurpose non-sag paintable Acrylic sealant. On exposure to atmosphere, acrylic sealant forms a durable elastomeric compound. A Green Building Product with Zero Percent VOC. It is a universal, one-component plasto-elastic acrylic adhesive sealant, curing by evaporation of water from the mass.
BENEFITS:
- Odorless and chemically neutral
- possibility of painting and grinding after curing
- possibility of applying multiple layers after curing
- exterior and interior applications
Uses of acrylic sealants
Paintablle Acrylic sealant, SUPEX 500 bonds well to a wide variety of substrates and are suitable for making permanent elastic seals of high adhesive strength. This acrylic Water based sealant is paintable, flexible. Acrylic sealant’s price is lesser than GP silicones.
- Gap of UPVC, PVC Joints.
- HVAC Duct sealing
- External and internal crack filler
- Walls and ceilings.
- skirting boards
- Concrete Expansion joints.
- Concrete, Granite Joints.
- Wood, Concrete, Granite,
- Aluminum, G I Sheet, M. S. Panel,
- Machinery Surface, Tiles , Coating,
- POP, U.B. Coat.
Some Synoynms of Acrylic sealant- Paintable sealant, window sealant, Duct sealant, door gap filler.
Hybrid MS Polymer sealants
What is MS polymer adhesive and sealant?
 MS polymer Sealants are highly elastic, high strength sealant. It has excellent adhesion to non-porous surfaces, will bond to damp surfaces and is paintable with most paints. Hybrid sealants are claimed to combine the strength of polyurethanes with the weathering resistance of silicones. In addition to their high performance properties, these sealants are achieving popularity due to their solvent-free and isocyanate-free nature and due to their formulation versatility that allows the customization of viscosity and early strength development for various applications.
MS polymer Sealants are highly elastic, high strength sealant. It has excellent adhesion to non-porous surfaces, will bond to damp surfaces and is paintable with most paints. Hybrid sealants are claimed to combine the strength of polyurethanes with the weathering resistance of silicones. In addition to their high performance properties, these sealants are achieving popularity due to their solvent-free and isocyanate-free nature and due to their formulation versatility that allows the customization of viscosity and early strength development for various applications.
- High bonding strength, instant bonding, low gap fill. Primarily used as a bonding agent than for sealing applications.
- Examples: Mirror Bonding, Panel Bonding, Cladding etc.
Benefits of MS polymer sealants
- High initial tack properties reduce the need for initial support.
- Fast curing, a quick build-up of end strength alongwith high sheer strength after full cure (no primer).
- Easy to apply and easy to tool and finish
- Remains elastic after curing.
- No odor.
- Does not contain neither isocyanates, silicones nor solvents.
- Paintable with all water-based paints.
- Excellent color stability. Likewise, weather and UV resistance.
- Good adhesion on wet substrates, bonds underwater.
What is a sealant used for?
Sealants are used in construction to prevent fluids and other substances from passing through material surfaces, joints, or openings. They can also prevent the passage of air, sound, dust, insects, and so on, as well as acting as a firestopping component.
What is the difference between adhesive and sealant?
How Do I Stop the Sealant from Failing?
According to the experts, sealants often cause around 90% of the problems, although they only account for 10% of the cost of a building project. Why?
Well sometimes sealants can fail. This can be due to issues with adhesives, cohesive or substrates. In simple terms, the bond between the sealant and substrate can fail, thus the substrate can break or the sealant can tear.These problems usually occur because of one or two errors. If you did not prepare the substrate effectively, or if you select the wrong product, the entire thing can fall apart. So before you choose a product, you should consider how you will use it.
Bibhas Agarwal
anaghaengineers.in@gmail.com
Whatsapp: 91 9833892782
Call : 91 9699892782
www.anaghaengineers.in
Adhesives & Sealants for Bus Body
The bus manufacturing industry is upgrading from mechanical fasteners and replacing them by adhesives and sealants . The shift towards adhesives and sealants in bus assembly processes is encouraged by the need for increased sustainability, use of composite materials, aerodynamic designs and safety regulations. .
Here you will find everything you need to know about adhesives and sealants used in different stages of bus manufacturing.
Bus Body adhesives sealants makes stronger, safer and lighter buses
Adhesives and sealants for buses are designed to meet the requirements of making the process and products stronger, safer, faster and lighter.
- Stronger: adhesives and sealants increase the durability of buses as they prevent corrosion unlike mechanical fasteners which are prone to cause galvanic corrosion.
- Safer:some adhesives and sealants are designed to damp impact, which makes them improve the buses´ crash test performance. Also fire retardant adhesives improve safety on board.
- Lighter: the use of adhesives and sealants instead of mechanical fasteners can lead to substiantial weight reduction. Adhesives make it possible to bond indifferent materials together without needing to worry about damaging either of the materials.
- Faster: not only allow adhesives and sealants for more aerodynamic designs, but they are also faster to process, which reduces the production time of buses.
Advantages of using Bus Body adhesives & sealants
- Smooth surface appearance and less rework
- Bonding dissimilar materials increasing design freedom
- Reduced risk of corrosion
- Increased comfort due to dampening sound and vibration
- Longevity and durability
- Reduced weight due to the elimination of mechanical fasteners
- Dampening sound and vibration
- Improved body stability and reduced fuel consumption due to lighter weight
- Increased impact safety in the event of a crash
- Resistance against extreme temperature conditions
- Design freedom due to thermoplastics
- Environmentally friendly bonding solutions
- Fast production process
- Cost reduction
- Improved aerodynamics
- Roof sealing, roof bottom sealing for mica bonding
- Roof gap sealing
- Side panel
- Floor bonding with plywood
- Dashboard bonding
- Plywood bonding in Driver cabin
- Rear FRP& FRP bumper
- front FRP
- Battery box sealing
- FRP stair sealing
- Vinyl bonding on to floor
- skirt panel bonding
- Side glass window frame pillar bonding
- front wind shield & rear wind shield
- Gap between window frames
- sealing beading on roof side
- ABS to frame
Applications of adhesive and sealant are continuously increasing. It is not only about making windows watertight but also keeping the body structure together. The adhesive and sealant applications not only focus on the frame, interior and exterior of the buses, but also contribute to the mechanisms under the hood including engine components and batteries. Below you will find the more specific applications of adhesives and sealants for buses.
Body structures
During the assembly of bus body structures, several adhesives and sealants are used in order to prevent corrosion, water ingress and standing water. They also contribute to comfort during long bus rides.
Adhesive & sealant solutions
There are easy to process, one component sealants such as MS polymers The growing demand for MS polymers is based on the need for environmentally friendly products.
Bus roof sealing and bonding
The roof is one of the most important parts of a bus, and the design still is one of the greatest challenges for bus manufacturers. Similar systems are also used to glue antennas and receivers on bus roofs.
Adhesives & sealants solutions
Bus roof sealing and bonding require flexible solutions which are not affected by whatever the environment might throw at the roof. The bus roof sealant and adhesive systems are often polyurethane based or hybrid systems. They exist as one and 2 component systems which allow for fast curing, speeding up the production process.
Bus floor sealing, side panels, luggage doors and hatches
Bus operators expect outstanding durability from their vehicle regardless the driving conditions. Therefore, the bus must be safe in possible crash situation and it should not degrade due to harsh climatic conditions.
Adhesive and sealant solutions
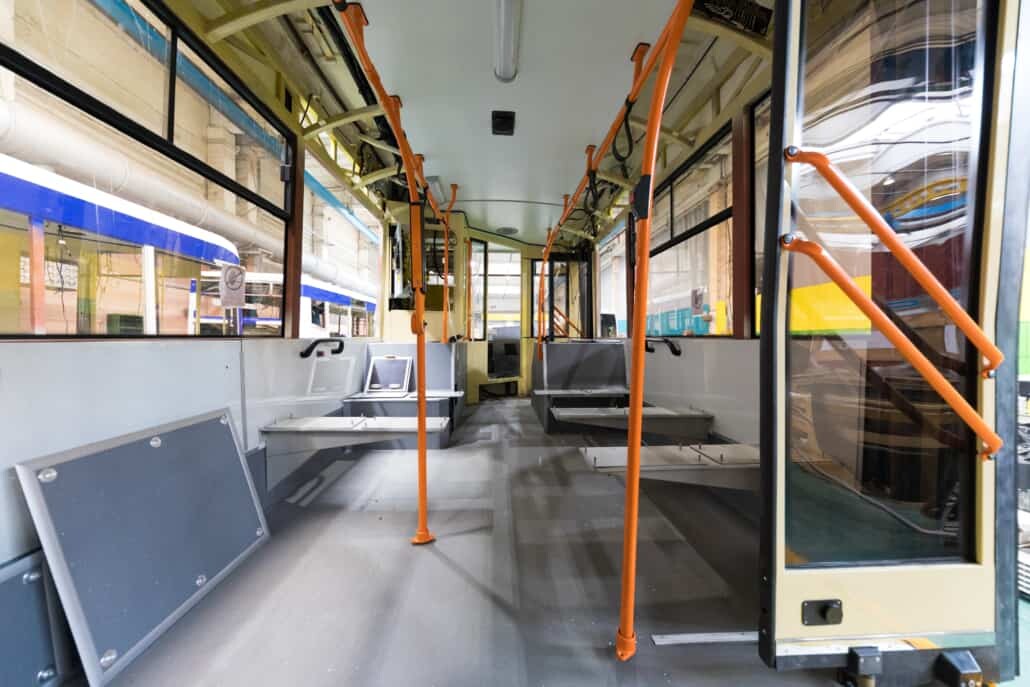

For sealing floors, side panels, luggage doors and hatches MS polymers are a common choice . The bonding of these applications is often realized with elastic polyurethane adhesives which cure fast and exist as one and two component systems. Also MMA adhesives are common for bonding interior panels.
Front and rear masks
The front and rear masks contribute to the aerodynamic design of buses. The use of adhesives and sealants instead of mechanical fasteners allows for more aerodynamic shapes and so contributes to reduced fuel consumption.
Adhesive and sealant solutions
Adhesives and sealants for front and rear masks of buses are usually thermoplastics which can be shaped when not completely cured. The solutions include polyurethane and hybrid systems which cure fast allowing for shorter processing times. The adhesive and sealant systems are usually one component solutions, which makes the processing less laborious.
Interior trim

The development of interior design of buses has lead to the use of ever-growing mix of plastics and fabrics which require durable and environmentally friendly bonding solutions. The adhesives for bus interior trim improve appearance and contribute to comfort.
Adhesive and sealant solutions
The most used adhesive for bus interiors is hot melt which appears in a solid phase in room temperature, and softens when heated. These adhesives allow for extremely fast processing. Hot melt adhesives are also used for example for furniture upholstery.
Bus direct glazing adhesive and sealant solutions
They are used for sealing and bonding direct glazing application as they provide fast curing times and high initial strength as well as contribute to aerodynamic design and stability of the vehicle. As the glazing of buses involves large and heavy surfaces, the adhesive must be chosen carefully opting for the highest quality. In some cases the direct glazing adhesive must be sealed using an appropriate sealant system. Gain more information on the best glazing adhesives and sealants!
Adhesive and sealant solutions
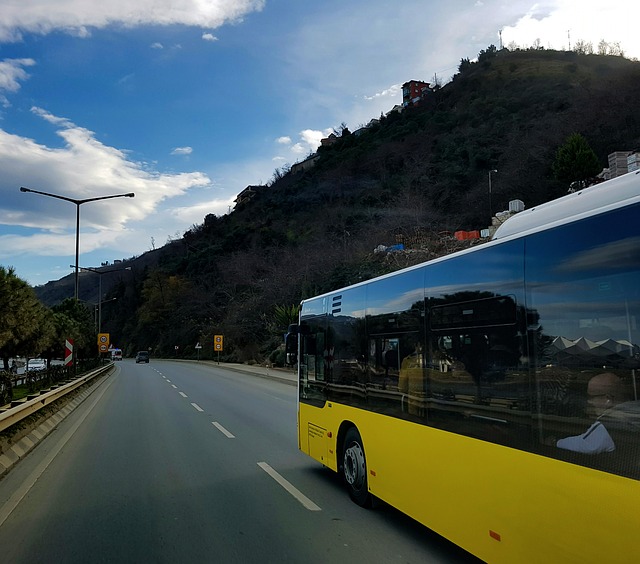

The products included MS polymers, silicone sealants and polyurethane based adhesives.
Adhesive & Sealant applications
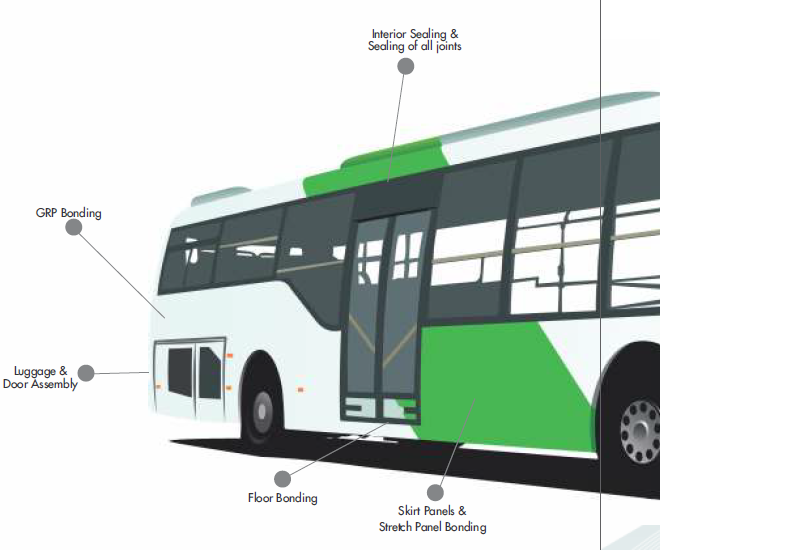
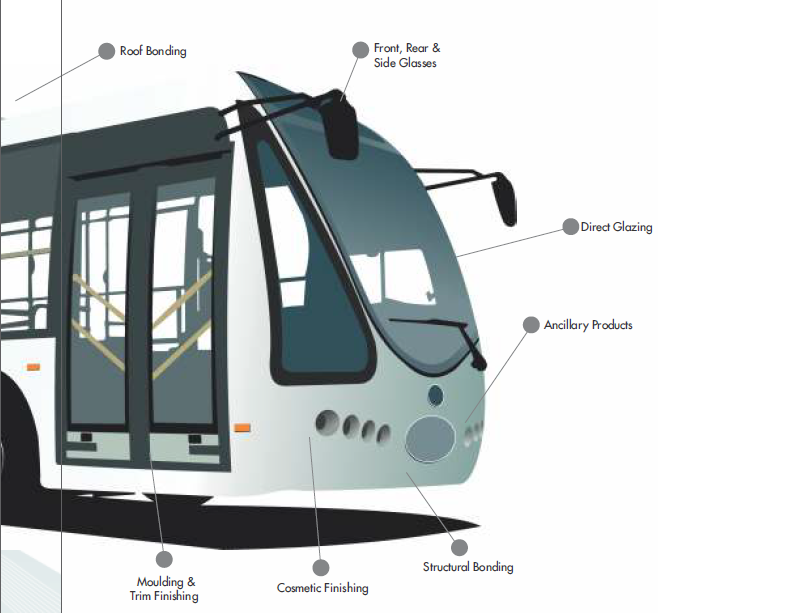
Pu adhesive sealant for auto glass/car windshield/bus body
Sheet metal, panel, FRP, Composites bonding
Boss PU 25 / Supex PU 25, Soudaflex 611, Soudaflex 621 – These PU Sealants are particularly designed for sealing application in areas including Bus & Coach, Truck, Earth moving Equipments, Tractor, Forklift, OEM, Repair Auto After Markets also various other commercial and industrial vehicles.
Further, it bonds a variety of material including FRP, GRP, timber, plywood, metals, particularly aluminium (including
anodized components), sheet steel (including phosphated, chromated and zinc-plated components), coated metals and paint coatings (two-part systems), ceramic materials as well as plastics.
Windscreen bonding, metal to glass Bonding
Supex PU 75 is a one-component, medium-modulus polyurethane sealant that cures on exposure to atmospheric humidity. Specially formulated for windscreen bonding applications. Suitable for glass bonding in trains and coachwork.It possesses excellent adhesion to all typical construction materials such as cement based materials, brick, ceramic, glass, wood, galvanized and painted sheet iron and various plastics.
BOSS PU 50 is a fast-curing one-component moisture curing polyurethane adhesive sealant that turns into a flexible, durable and resistant elastomeric seam and has a very good adhesion to most industrial materials. It has high elasticity and excellent tear, vibration and weathering resistance. Easy to apply, it adheres without primer to the most common substrates, such as glass, anodized aluminum, lacquered metal, wood, FRP, and concrete.
Kindly post your questions/ queries in the comment section or contact me at:
Bibhas Agarwal
anaghaengineers.in@gmail.com
Whatsapp: 91 9833892782
Call : 91 9699892782
www.anaghaengineers.in